Cord Blood for Liver Disease Therapy
Stem cell therapy is a form of regenerative medicine that uses stem cells to treat, manage, or prevent a medical condition. It stimulates a repair response in damaged or diseased tissue. Currently, hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the only stem cell treatments approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
HSCs have been used in treatments for various conditions, including leukemias, lymphomas, bone marrow cancers, and more. Additionally, researchers are conducting clinical trials regarding stem cell treatment for cirrhosis and other liver diseases.
The Impact of Liver Disease
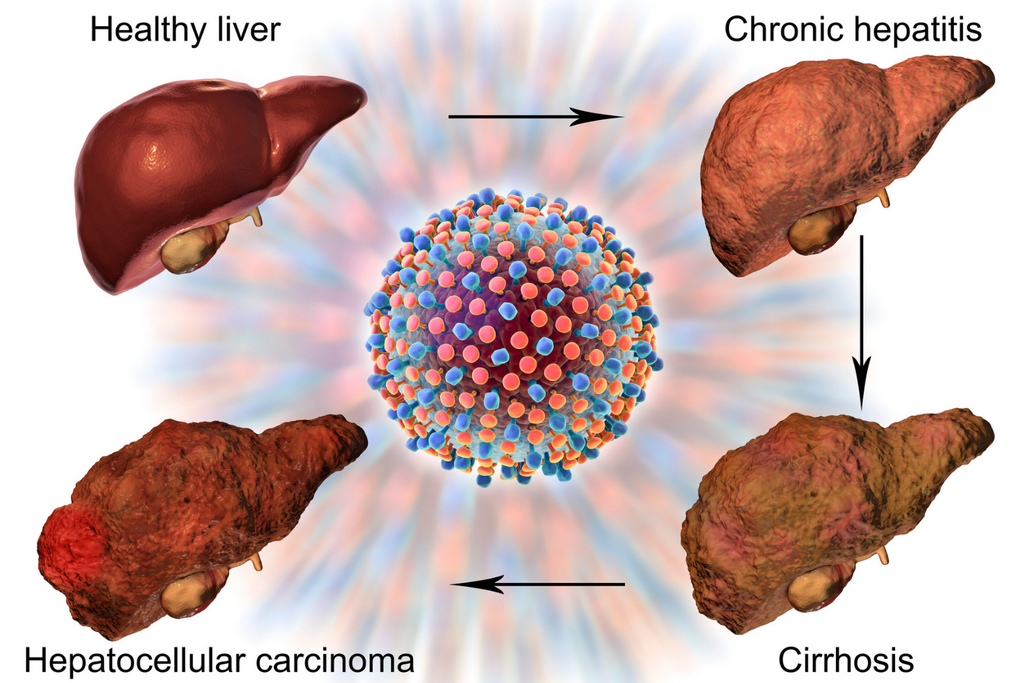
Cirrhosis is a late-stage disease that involves permanent liver scarring and damage. Scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, blocking blood flow and preventing the organ from functioning correctly.
Cirrhosis affects roughly one in 400 U.S. adults, primarily those aged 45-54. People with a history of alcohol misuse, obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, or hepatitis B or C infection are at higher risk of developing this disease. As it progresses, it can lead to liver failure.
Because people with liver disease typically don’t experience symptoms until it reaches advanced stages, they often aren’t even aware they have it. Depending on how well the liver works, they may encounter no symptoms, or these signs may occur gradually. Cirrhosis is often detected by chance during an X-ray, blood drawing, or another procedure.
Symptoms of Liver Disease
Here are some early indicators of liver disease:
- Poor appetite and weight loss
- Stomach pain or nausea
- Spider angioma (abnormal blood vessel clusters) on the skin
- Fatigue and low energy
As liver function declines, a person may experience:
- Yellow discoloration in the eyes (jaundice), skin, or mucous membranes.
- Fluid buildup in the legs (edema) or abdomen (ascites).
- Abnormal bleeding and bruising, usually from swollen veins in the digestive tract.
- Redness in the palms of the hands.
- Problems with concentration and memory.
- Pale or clay-colored stools.
Damage from cirrhosis is permanent. However, the liver is a large organ. If part of it remains functional, a patient may be able to slow the progression of the disease with stem cell treatment.
Stem Cell Treatment for Liver Disease
Though liver disease is a global health concern, it’s especially prevalent in China, affecting 300,000 to 400,000 people annually. Based on the outcomes of 10 trials conducted in the People’s Republic of China, liver cirrhosis patients who underwent cord blood transplantation showed better improvement than those who received traditional therapies alone.
Out of 616 people who participated in these studies, 327 received a combination of cord blood and routine treatments. The remaining 289 received traditional therapies exclusively. Researchers obtained the cells from healthy, full-term infants’ umbilical cord blood. They then infused these cells into patients through the portal vein, hepatic artery, or peripheral vein.
Additionally, this research showed that cord blood transfusion could improve liver function without significant side effects. Fever was the most common side effect during treatment, and it typically subsided naturally within 24 hours.
Umbilical Cord Blood vs. Bone Marrow Stem Cell Therapy
In preclinical stem cell transplantation studies, the most commonly used cells were HSCs, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and hepatic progenitor cells (HPCs). These were typically obtained from autologous (self) or allogeneic (donated) bone marrow.
However, extracting stem cells from bone marrow is an invasive procedure. Stem cells from umbilical cord blood are more accessible than those from bone marrow, making it a more viable source. Umbilical cord blood stem cells contain HSCs, MSCs, and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). They can migrate to different injury sites and differentiate into various cell types.
Routine vs. Stem Cell Therapies
Traditional liver therapies typically involve lifestyle modifications like weight loss, dieting, or alcohol abstinence. Other liver issues may be addressed with medications and pain relievers.
Some cases might warrant surgery, where a portion of a living donor’s liver is removed to replace a patient’s damaged liver. Following the procedure, the donor’s liver regenerates back to its original size. Likewise, the patient’s new liver grows to a normal size.
Stem cell liver transplantation is believed to stimulate new liver cell growth while slowing the loss of existing liver cells. Results from the studies showed that cord blood stem cells helped enhance liver regeneration, improving patients’ quality of life.
Based on these clinical trials and research, stem cell therapy combined with routine treatments appears to be a promising option for patients with liver disease.
How Does Stem Cell Therapy for Liver Disease Work?
Simply put, liver stem cell transplantation stimulates the growth of new cells while stopping the death of current ones. Stem cells can differentiate or “develop” into different cell types within the body. They can seek out diseased or infected liver tissue, then work to regenerate the organ.
HSCs can differentiate into any of the body’s blood cells and cellular blood components, including red and white blood cells and platelets. Meanwhile, MSCs are multipotent stem cells that can renew into cell types like muscle, cartilage, adipose tissue, neurons, tendons, and ligaments.
HSCs and MSCs are present in bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, and placental tissue. Both cell types stimulate tissue regeneration in injured areas. Unlike HSC-based treatments, however, MSC therapies aren’t currently FDA-approved.

The Future of MSC Therapies for Liver Disease
Researchers are optimistic about MSCs’ future role in cellular repair for cirrhosis. Currently, they are performing extensive research for MSC treatment for liver disease and other medical conditions, including the following:
- Bone and cartilage injuries
- Heart disease
- Lung cancer
- Parkinson’s disease
- Stroke damage
- Type 1 diabetes
- Spinal cord injuries
Though MSC treatments haven’t yet been FDA-approved, they have been approved for treatment in countries such as Canada, South Korea, Japan, India, and New Zealand. Over 300 MSC clinical trials are being conducted around the globe.
Because these cells have the unique ability to differentiate into multiple cell and tissue types, many scientists and researchers believe they will radically transform the medical field.

Trust Americord for Cord Blood Storage
At Americord®, we extract and store stem cells from umbilical cord blood, cord tissue, and placental tissue. By choosing us for cord blood banking, you or a family member can use these preserved stem cells for medical or therapeutic applications when needed. Stem cells show great promise for diseases like liver cirrhosis and many other medical conditions.
We’re passionate about helping people live long, healthy lives. Our clients’ well-being and satisfaction are our greatest priorities, which is why we constantly strive to assess and enhance our customer service. Additionally, our team pursues partnerships and research to continue expanding the stem cell regenerative medicine field.
If you are pregnant and are looking for more information about newborn stem cell banking, give one of our Stem Cell Specialists a call (866-503-6005) today! You can also learn more here on our website.
The views, statements, and pricing expressed are deemed reliable as of the published date. Articles may not reflect current pricing, offerings, or recent innovations.




